
The aim of this paper is to report the case of a six-year-old boy that presented a greenstick fracture of the mandibular body, and its conservative management with longitudinal follow-up during a year.Ī healthy six year-four months old male attended dental service at the Postgraduate Pediatric Dentistry Clinic of San Luis Potosi University, San Luis Potosi, Mexico complaining of suffering an accident where he was hit by a running motorcycle while the boy was walking through a dirt road. So, it can be said that children aren’t just “small adults”, due to the anatomical, physiological and psychological factors. Many injuries that require surgical management in adults, could be conservatively managed in children. In general, the lower calcification allows the pediatric bones to be flexed in response to external forces, producing greenstick fractures, where one bone cortex will be broken and the other one will be bent, without losing bone continuity. The most affected bones are the nasal bone and the mandible, with an incidence of 60%. Nevertheless, it is common that pediatric maxillofacial fractures develop after a traumatism. The pediatric body has many features that provide protection and resilience to traumatic forces in craneofacial injuries, in comparison to adults, such as a wider forehead and cranial mass that cover the face, fibroelastic bone tissue with more cancellous bone ratio and non-erupted permanent dentition that offers more stability.

In fact, head wounds could appear due to pediatric traumas, because head is the most common body part involved in accidents. 1ĭuring the first years of life, children are not exempt from suffering injuries that could threaten their optimal growth and development, becoming our most vulnerable population at that stage. The longitudinal follow-up during a year showed a good prognosis in mandible growth and development. The management was conservative: analgesic and anti-inflammatory therapy, soft diet, physical activities restriction and compliance with oral hygiene.
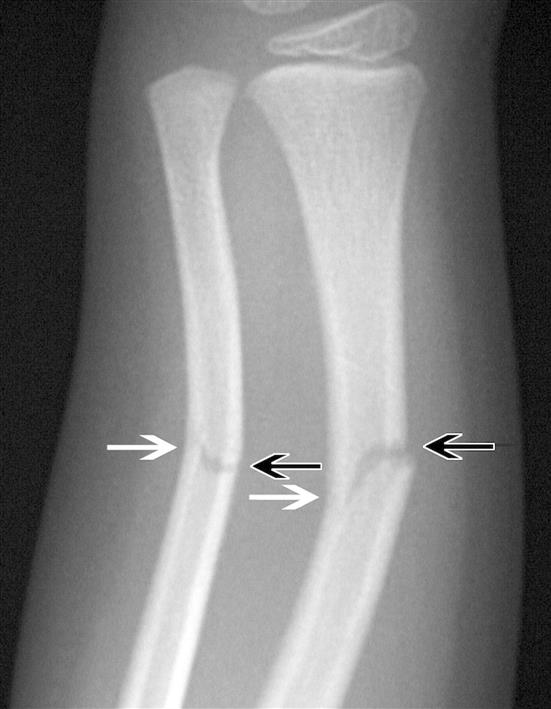
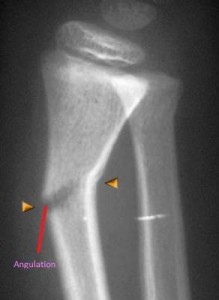
Radiographic exams confirmed an incomplete fracture line without displacement next to the permanent mandibular left first molar. At clinical examination, it was observed an increase in mandibular left angle volume and intraoral lacerations. This is a case report of a six-year-old boy that presented a greenstick fracture of the mandibular body due to a vehicle accident. Many injuries that require surgical management in adults, could be conservatively managed in children due to anatomical, physiological and psychological factors. The lower calcification of pediatric bones allows them to be flexed in response to external forces, producing greenstick fractures. It is common that pediatric maxillofacial fractures develop after a traumatism.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
